WHAT IS COMPUTER NETWORK ?
A computer network is an interconnection among two or more computers or computing devices. Such interconnection allows computers to share data and resources among each other. A computer network can include different types of hosts (also called nodes) like server, desktop, laptop, cellular phones.

EVOLUTION OF COMPUTER NETWORK
- A network additionally enables associated PCs to share documents and information and also equipment assets, i.e., scanners, plotters, projectors, and storage devices, making it simpler to gather and administer data, and enabling clients to work together.
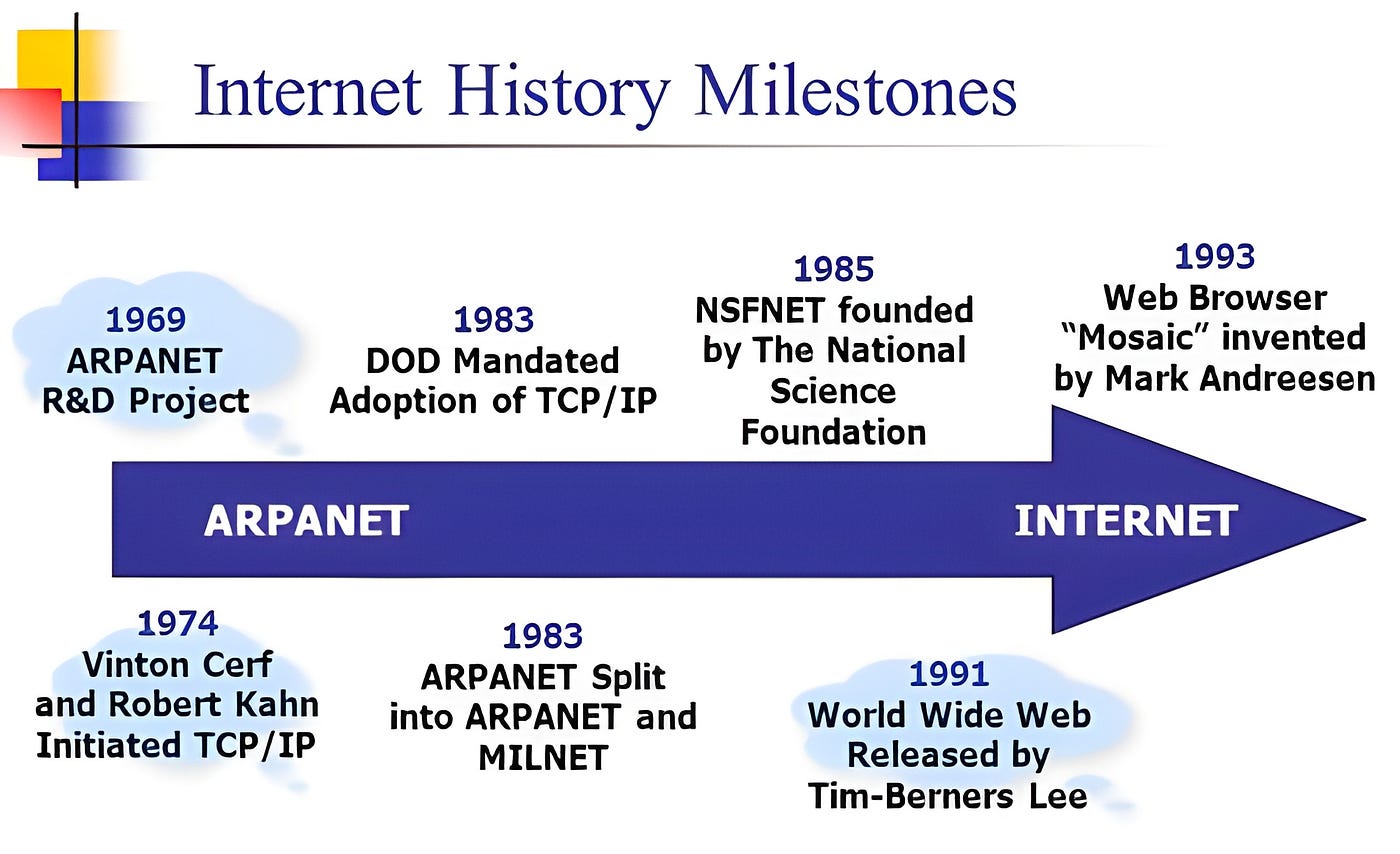
- Advancement of systems administration began path back in 1969’s with the improvement of the first system called ARPANET, which prompted the improvement of the web.
- At that point, constant everyday upgradation occurs in the system innovation.
ARPANET
- ARPANET stands for ADVANCED RESEARCH PROJECTS AGENCY NETWORK.
- ARPANET was the network that became the basis for the Internet.
- It was the first network that came into existence in 1969, which was designed and named by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) and the US Department of Defence (DoD).
- The first message was communicated between the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and Stanford Research Institute (SRI).
NSFNET
- NSFNET stands for NATIONAL SCIENCE FEDERATION NETWORK.
- In the mid-’80s another federal agency, NSFNET created a new network that was more capable than ARPANET and became the first backbone infrastructure for the commercial public Internet.
- Its main aim was to use networks only for academic research and not for any kind of private business activity.
SOME INTERESTING DATES:
- 1982: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP), as the protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, emerge as the protocol for ARPANET.
- 1986: The National Science Foundation’s NSFNET goes online to connected supercomputer centers at 56,000 bits per second — the speed of a typical dial-up computer modem.
- 1991: CERN introduces the World Wide Web (WWW) to the public.
- 1992: The first audio and video are distributed over the internet. The phrase "surfing the internet" is popularized.
- 1994: Netscape Communications is born. Microsoft creates a Web browser for Windows 95.
INTERNET
- The internet has evolved from ARPANET. The internet is a globally connected network system that utilizes TCP/IP
to transmit information. - It allows computers of different types to exchange information and is known as the internet.
- The Internet is the financial communications method on the planet, in which the following services are instantly available:
- Web-enabled audio/video conferencing services
- Online movies and gaming
- Data transfer/file-sharing, often through File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Social networking

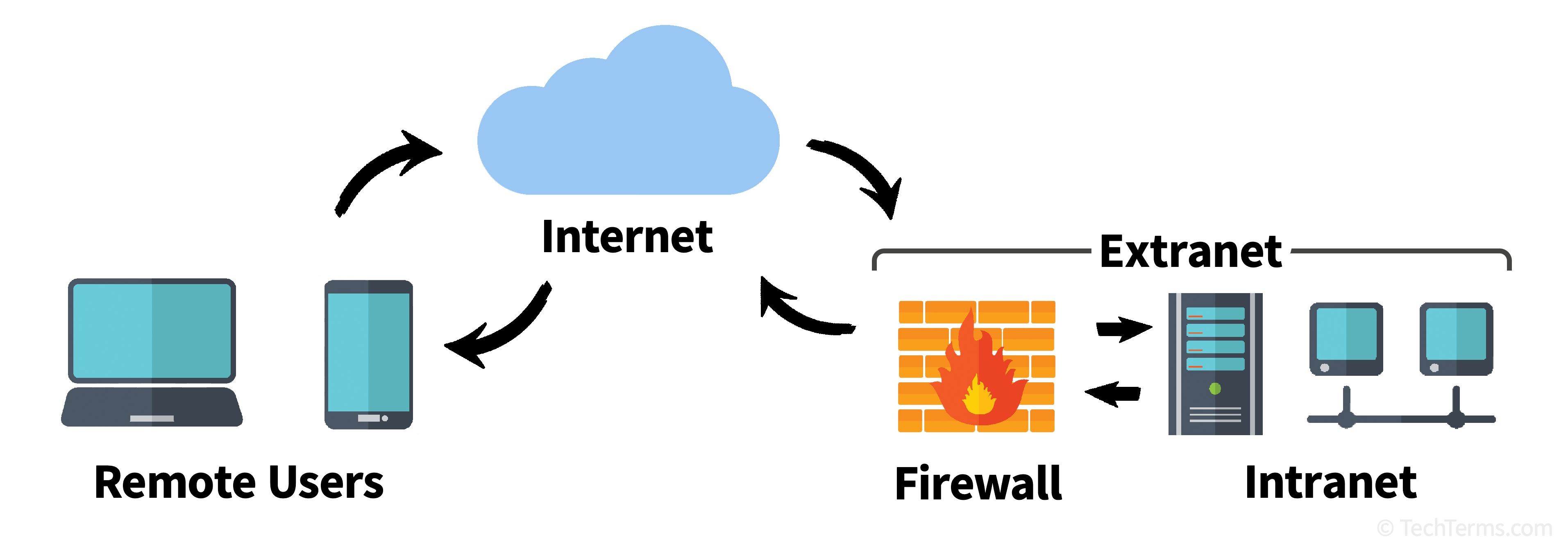
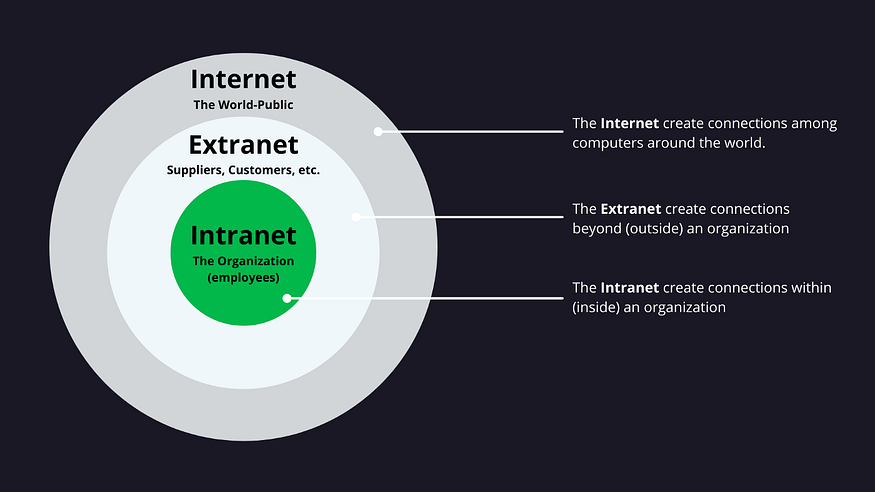
INTRANET
- An intranet is a private network contained within an enterprise that is used to securely share company information and computing resources among employees.
- An intranet can also be used for working in groups and teleconferences.

EXTRANET
- An extranet is an intranet that grants access to those outside of an organization to certain information and applications.
- An extranet is a controlled private computer network that allows communication with business partners, vendors and suppliers or an authorized set of customers.
INTERNET, INTRANET AND EXTRANET
TYPES OF AREA NETWORK
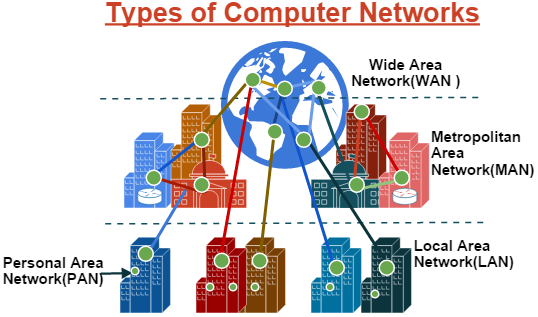
- The Network allows computers to connect and communicate with different computers via any medium.
- LAN, MAN, and WAN are the three major types of networks designed to operate over the area they cover.
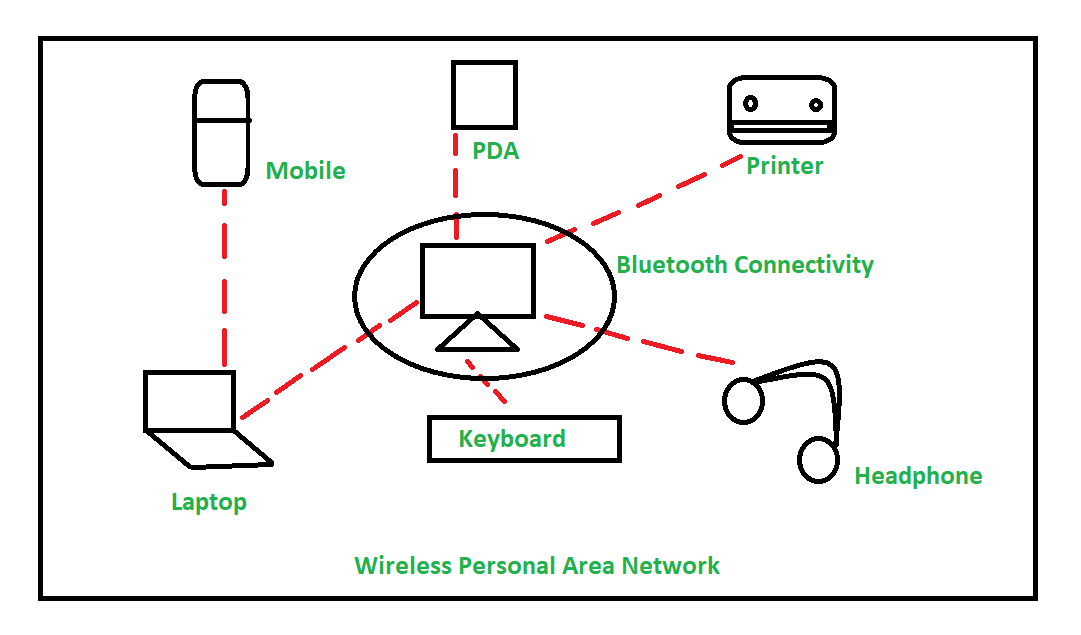
PAN (PERSONAL AREA NETWORK)
- PAN is a personal area network having an interconnection of personal technology devices to communicate over a short
distance. It covers only less than 10 meters or 33 feet of area. - A Personal Area Network typically involves a computer, phone, tablet, printer, PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) and other and other entertainment devices like speakers, video game consoles, etc.
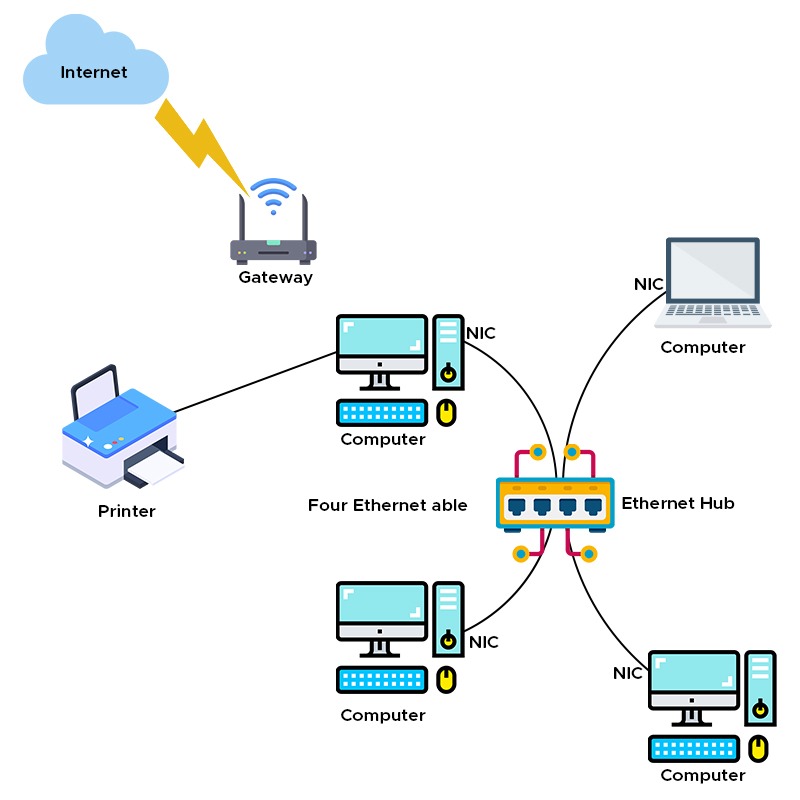
LAN (LOCAL AREA NETWORK)
- LAN or Local Area Network connects network devices in such a way that personal computers and workstations can share data, tools, and programs.
- LANs cover a smaller geographical area (Size is limited to a few kilometers) and are privately owned.
- One can use it for an office building, home, hospital, school, etc.
- Data transfer in LAN is quite high, and usually varies from 10 Mbps (called Ethernet) to 1000 Mbps (called Gigabit Ethernet).
- There is a standard for wireless LANs called IEEE 802.11, popularly known as WiFi.
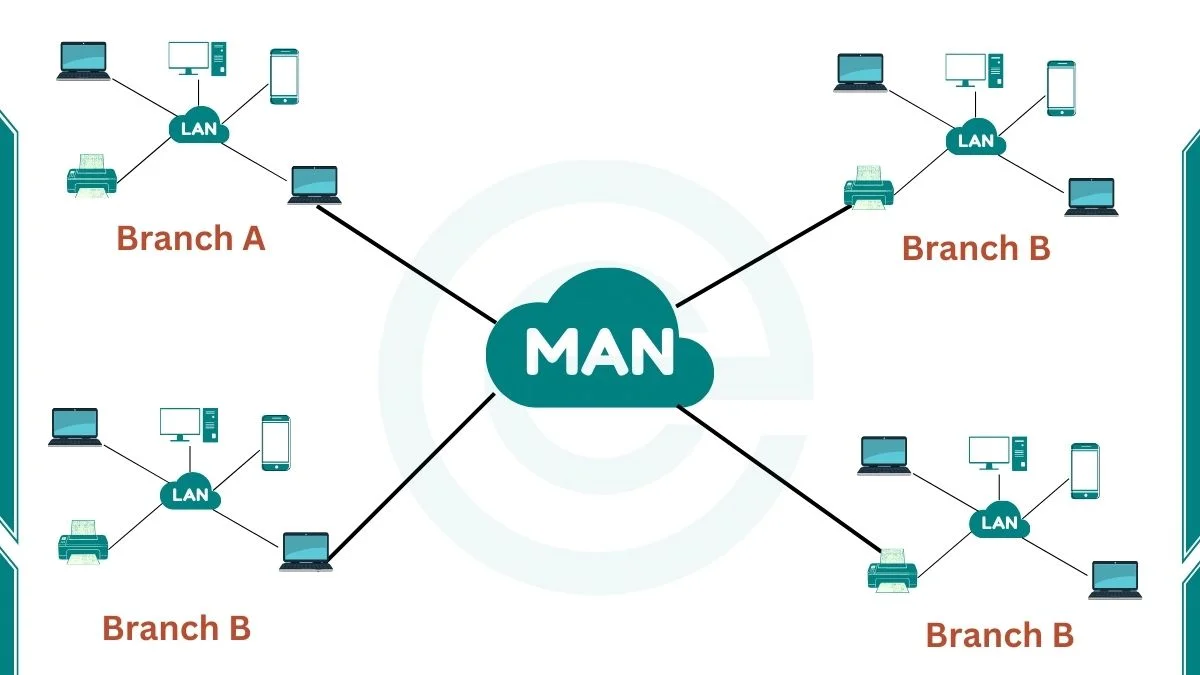
MAN (METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK)
- MAN or Metropolitan area Network covers a larger area than that covered by a LAN and a smaller area as compared to WAN.
- MAN has a range of 5-50km. It connects two or more computers that are apart but reside in the same or different cities.
- In highspeed wireless Internet access have resulted in another MAN, which has been standardized as IEEE 802.16 and is popularly known as WiMAX.
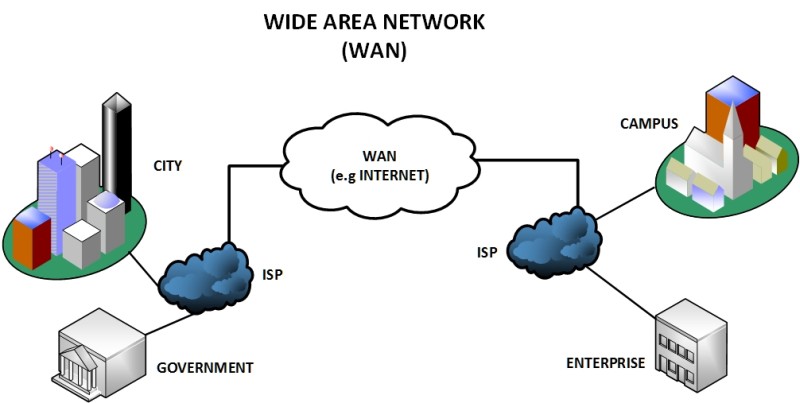
WAN (WIDE AREA NETWORK)
- WAN or Wide Area Network is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area, although it might be confined
within the bounds of a state or country. - WAN has a range of above 50 km.
- A WAN is essentially a network of networks, with the Internet the world's largest WAN.
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
- Network topology is physical and logical structure of the network's connections and nodes.
- Network topology impacts network performance, security and scalability, making it a crucial concept in network design and management.
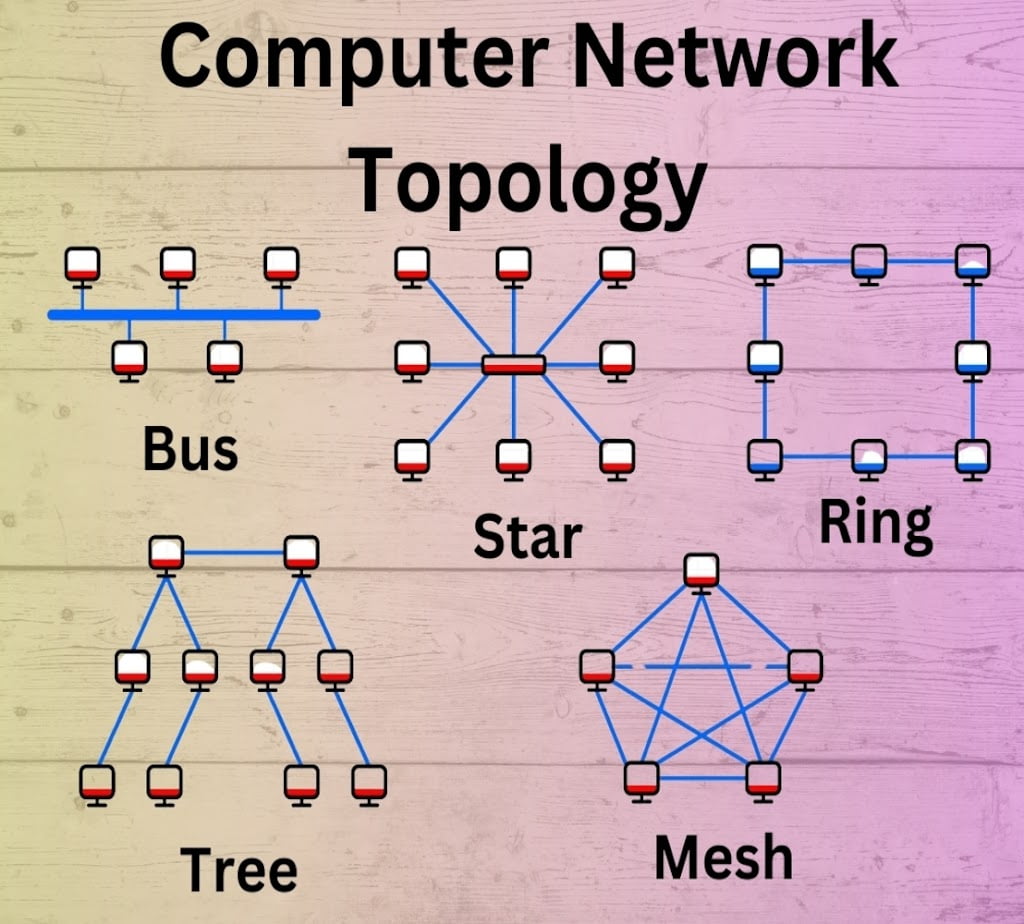
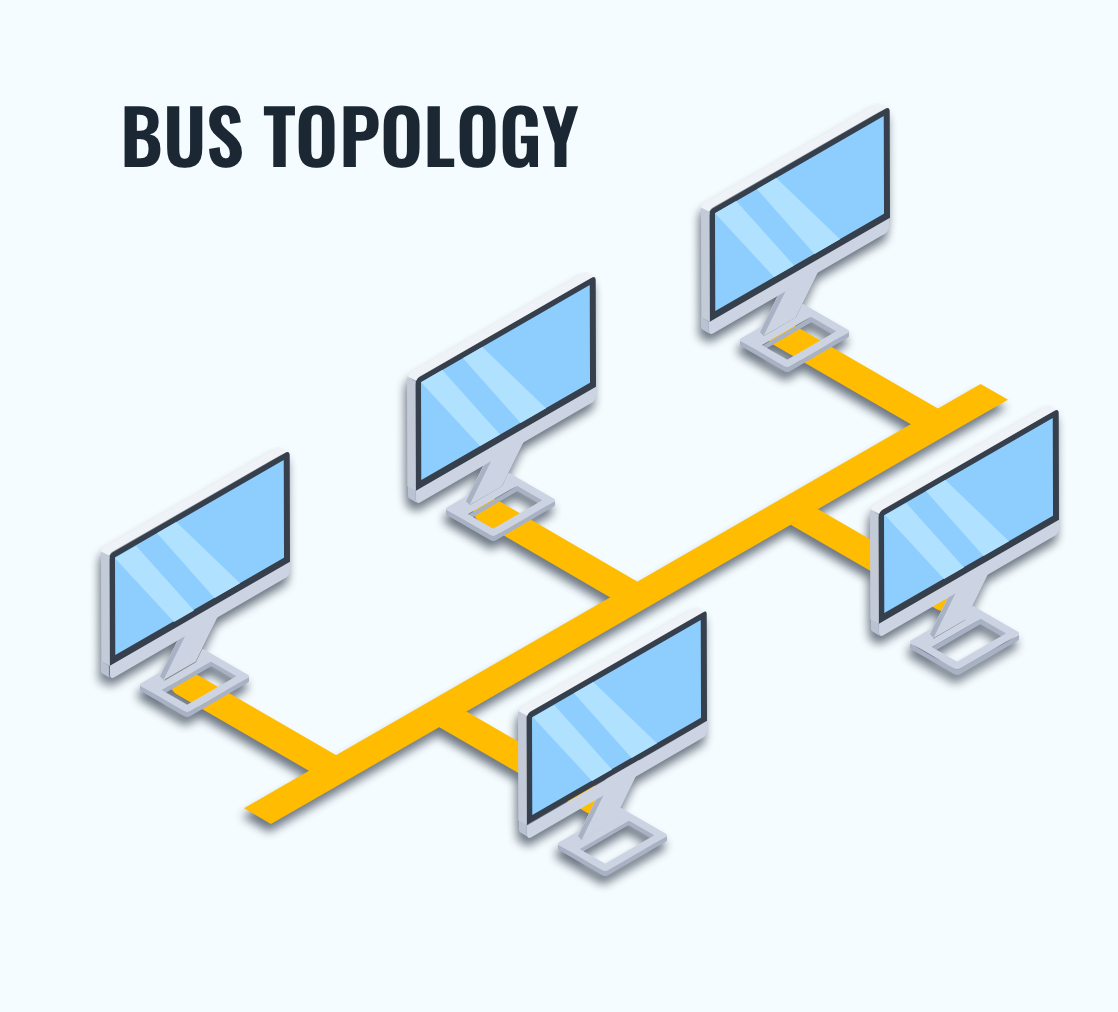
BUS TOPOLOGY
- All of the devices in a bus topology network are linked together by a single cable, which is referred to as a “bus” and the cable is known as backbone cable.
- It is bi-directional.
- It is a multi-point connection.
- Bus topology is uncomplicated and inexpensive, making it ideal for small networks.
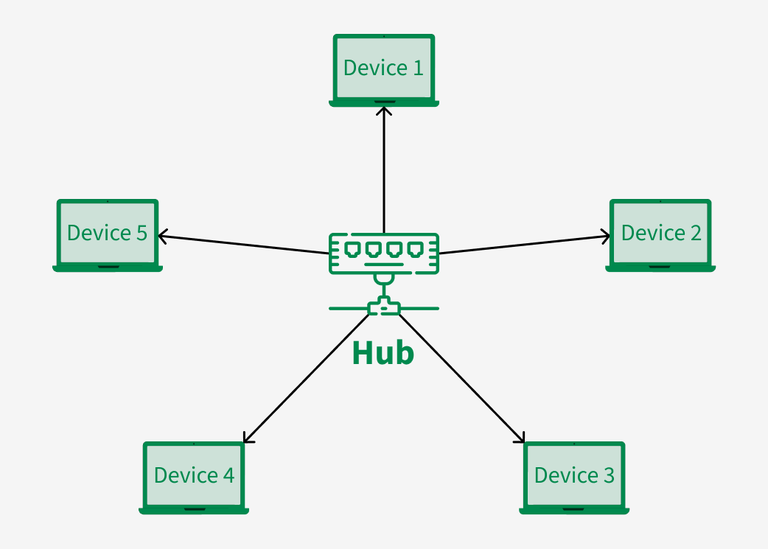
STAR TOPOLOGY
- All the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable.
- This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node.
- In Star Topology, many popular Ethernet LAN protocols are used as CD(Collision Detection), CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access), etc.
RING TOPOLOGY
- It forms a ring connecting devices with exactly two neighboring devices.
- The data flows in one direction, i.e. it is unidirectional.
- But it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology.

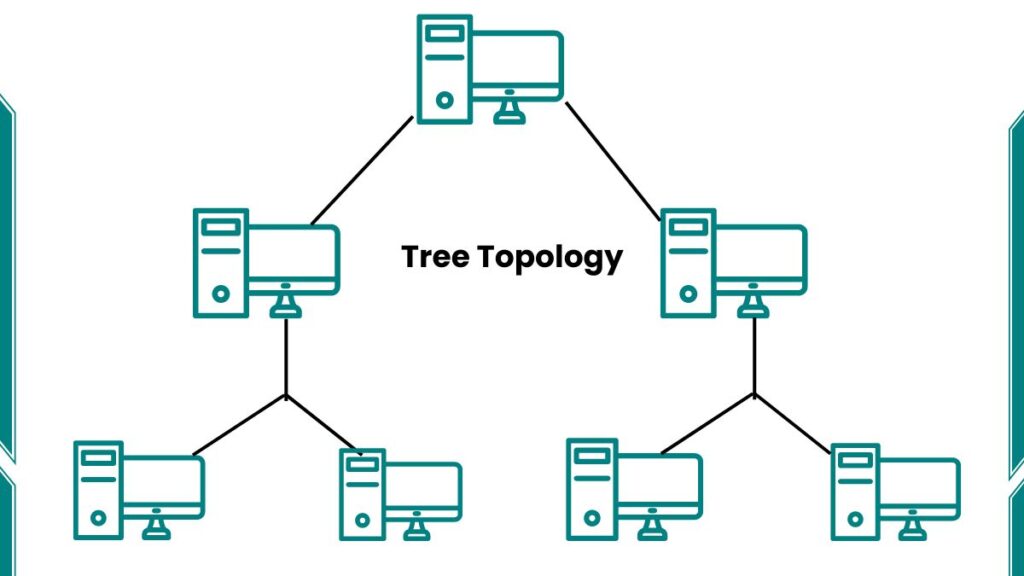
TREE TOPOLOGY
- This topology is the variation of the Star topology. This topology has a hierarchical flow of data.
- It resembles a tree with a root node and various branches. The root node is connected to multiple levels of child nodes, forming a hierarchy.
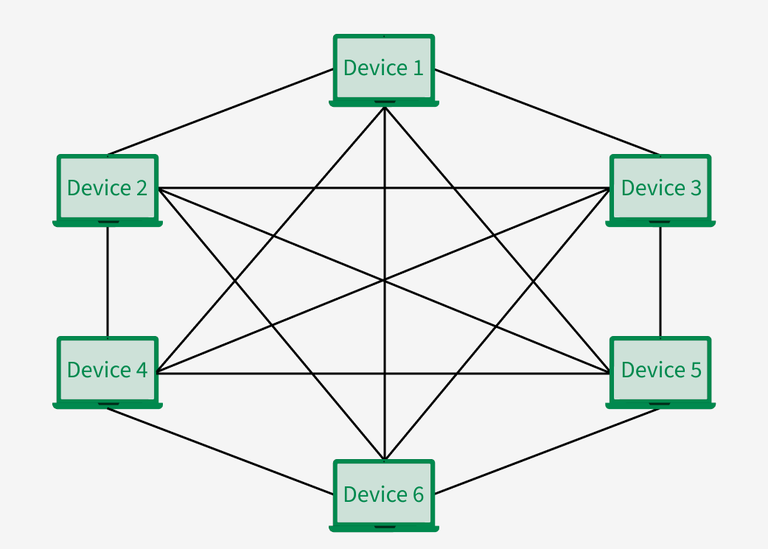
MESH TOPOLOGY
- In a mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via a particular channel.
- The nodes are connected to each other completely via a dedicated link during which information travels from nodes to nodes.
- A mesh network comprises multiple devices or nodes connected in a non-hierarchical manner so that they can coexist, cooperate, and provide comprehensive network coverage to a broader area than possible by a single router.
NETWORK DEVICES
- Network devices, also known as networking hardware, are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with one another.
- For example Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Routers,Gateway and NIC, etc.

MODEM
- MODEM stands for Modulator/Demodulator. The modem is defined as a networking device that is used to connect devices connected in the network to the Internet.
- The main function of a modem is to convert the analog signala that come from telephone wire into a digital form.
- The modem is also known as a signal translator as it translates one signal into another signal by modulating the digital signals into an analog signal for transmission and then demodulates receiving analog signals into digital signals.
![]()
REPEATER
- A repeater is a networking device that helps to regenerate signals to increase the reach of a network.
- One of the primary benefits of repeaters is the error free transfer of data over longer distances.
- Its main function is to amplify (i.e., regenerate) the signal over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted over the same network.

SWITCH
- A switch is a data link layer networking device which connects devices in a network and uses packet switching to send and
receive data over the network. - A network switch is a hardware component responsible for relaying data from networks to the destination endpoint through packet switching, MAC address identification, and a multiport bridge system.

ROUTER
- A router is a device like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses.
- The router is mainly a Network Layer device.
- By sending data packets to their intended IP addresses, it manages traffic between different networks and permits several devices to share an Internet connection.








