WHAT IS INTERNET PROTOCOL ?
Internet protocols are a set of rules that allow computers and other devices to communicate over the Internet. These protocols ensure that data is sent, received, and understood correctly between different systems. There are many types of internet protocols, each serving a specific purpose, such as transferring files, sending emails, or securing data.

- Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of rules that allows devices to communicate with each other over the Internet.
- Every device connected to the internet has a unique IP address that helps data know where to go and where it is coming from.
- An IP address represents an Internet Protocol address. An IP address helps the Internet to distinguish between different routers, computers, and websites.
- When you send information over the internet, IP split it into small parts called packets. Each packet contains a piece of the data and the address of where it needs to go.
TYPES OF INTERNET PROTOCOL (IP)
TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol)
- In TCP/IP, the IP protocol ensures that each computer that is connected to the Internet is having a specific serial number called the IP address.
- TCP specifies how data is exchanged over the internet and how it should be broken into IP packets.
- It also makes sure that the packets have information about the source of the message data, the destination of the message data, the sequence in which the message data should be re-assembled, and checks if the message has been sent correctly to the specific destination.

SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- SMTP protocol is important for sending and distributing outgoing emails.
- This protocol uses the header of the mail to get the email id of the receiver and enters the mail into the queue of outgoing mail.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- This protocol is used for transferring files from one system to the other.
- File transfer protocol (FTP) is a network communication protocol that enables the delivery of digital files from a server to the client, authenticated by a plaintext (unencrypted) sign-in process.
- This works on a client - server model.
- When a machine requests for file transfer from another machine, the FTO sets up a connection between the two and authenticates each other using their ID and Password.
HTTP(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)
- HTTP protocol is used to transfer hypertexts over the internet and it is defined by the www(world wide web) for information transfer.
- This protocol defines how the information needs to be formatted and transmitted. And, it also defines the various actions the web browsers should take in response to the calls made to access a particular web page.
- Whenever a user opens their web browser, the user will indirectly use HTTP as this is the protocol that is being used to share text, images, and other multimedia files on the World Wide Web.
HTTPS(HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure)
- HTTPS is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
- It is used for secure communication over a computer network with the SSL/TLS protocol for encryption and authentication.
- So, generally, a website has an HTTP protocol but if the website is such that it receives some sensitive information such as credit card details, debit card details, OTP, etc then it requires an SSL certificate installed to make the website more secure.
- So, before entering any sensitive information on a website, we should check if the link is HTTPS or not. If it is not HTTPS then it may not be secure enough to enter sensitive information.

TELNET(Terminal Network)
- TELNET is a standard TCP/IP protocol used for virtual terminal service given by ISO.
- TELNET operation lets us display anything being performed on the remote computer in the local computer.
- This operates on the client/server principle. The local computer uses the telnet client program whereas the remote computer uses the telnet server program.
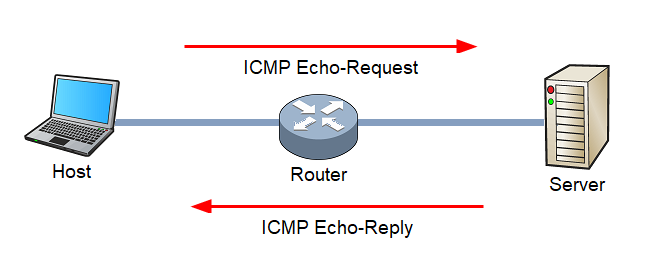
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a network protocol that is used to send error messages and operational information about network conditions.
- It is an integral part of the Internet Protocol (IP) suite and is used to help diagnose and troubleshoot issues with network connectivity.
- ICMP messages are typically generated by network devices, such as routers, in response to errors or exceptional conditions encountered in forwarding a datagram.
- ICMP can also be used by network management tools to test the reachability of a host and measure the round-trip time for packets to travel from the source to the destination and back.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is a protocol used for retrieving emails from a mail server.
- It allows users to access and manage their emails on the server, rather than downloading them to a local device.
- This means that the user can access their emails from multiple devices and the emails will be synced across all devices.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless, unreliable transport layer protocol.
- Unlike TCP, it does not establish a reliable connection between devices before transmitting data, and it does not guarantee that data packets will be received in the order they were sent or that they will be received at all.
- Instead, UDP simply sends packets of data to a destination without any error checking or flow control.
- UDP is typically used for real-time applications such as streaming video and audio, online gaming, and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) where a small amount of lost data is acceptable and low latency is important.
- UDP is faster than TCP because it has less overhead. It doesn’t need to establish a connection, so it can send data packets immediately.
POP3(Post Office Protocol 3)
- It has two Message Access Agents (MAAs) where one is client MAA (Message Access Agent) and another is server MAA(Message Access Agent) for accessing the messages from the mailbox.
- This protocol helps us to retrieve and manage emails from the mailbox on the receiver mail server to the receiver’s computer.
- The POP3 works on two ports i.e port 110 and port 995.
IPv4
- The fourth and initially widely used version of the Internet Protocol is called IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4).
- It is the most popular version of the Internet Protocol and is in charge of distributing data packets throughout the network.
- Maximum unique addresses for IPv4 are 4,294,967,296 (232), which are possible due to the use of 32-bit addresses.
- The network address and the host address are the two components of each address. The host address identifies a particular device within the network, whereas the network address identifies the network to which the host belongs.
IPv6
- The most recent version of the Internet Protocol, IPv6, was created to address the IPv4 protocol’s drawbacks.
- A maximum of 4.3 billion unique addresses are possible with IPv4’s 32-bit addresses. Contrarily, IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, which enable a significantly greater number of unique addresses.
- This is significant because IPv4 addresses were running out and there are an increasing number of devices that require internet access.
- IPv6 offers enhanced security features like integrated authentication and encryption as well as better support for mobile devices.
/IPv4-vs-IPv6-EN.png?width=1320&name=IPv4-vs-IPv6-EN.png)
Gopher
- Gopher is a type of file retrieval protocol that provides downloadable files with some description for easy management, retrieving, and searching of files.
- All the files are arranged on a remote computer in a stratified manner. It is an old protocol and it is not much used nowadays.

Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- Voice over Internet Protocol or VoIP, allows us to have voice call (telephone service) over the Internet, i.e., the voice transmission over a computer network rather than through the regular telephone network.
- It is also known as Internet Telephony or Broadband Telephony.
- This innovative technology converts your voice into digital data packets, which are transmitted via broadband connections.
- VoIP not only offers significant cost savings on both domestic calls and international calls but also provides a suite of advanced features such as call forwarding, voicemail-to-email, and video conferencing.
- Voice is converted into a digital signal by VoIP services that travel over the Internet. If the regular phone number is called, the signal is converted to a regular telephone signal i.e. an analog signal before it reaches the destination.








